
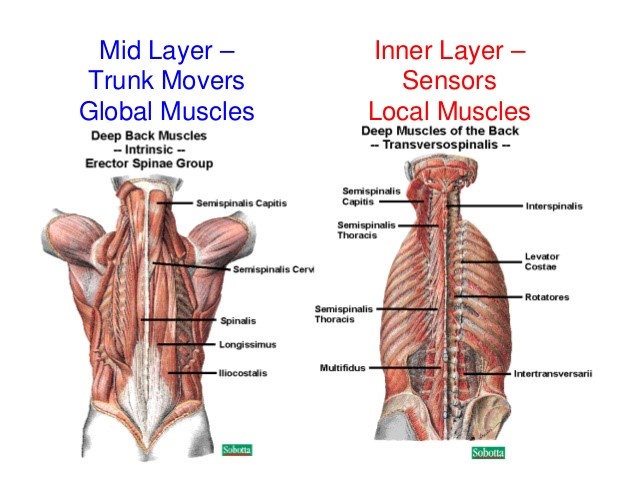
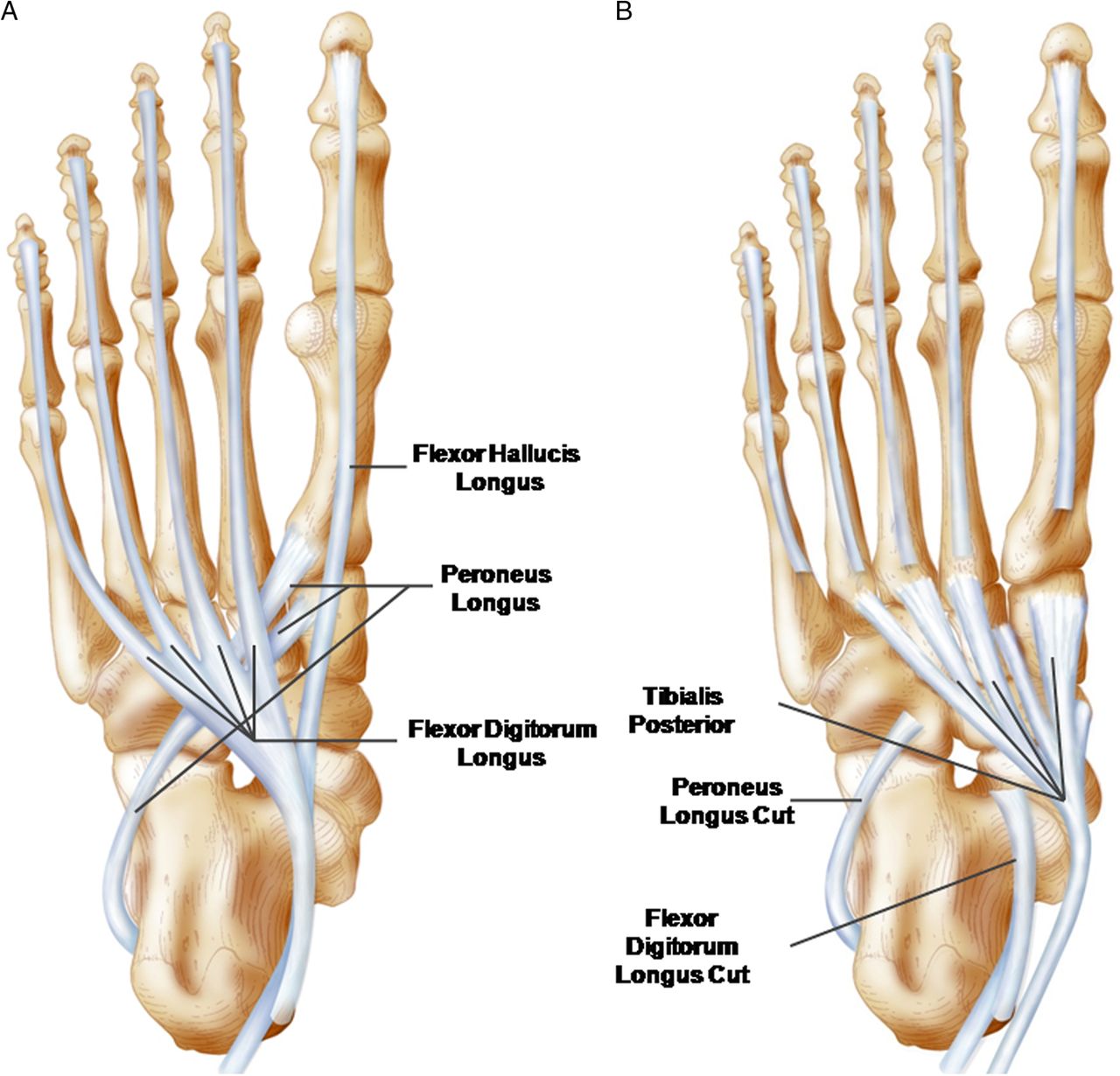
Crossing the ankle joint, these muscles are divided into Superficial Posterior, Deep Posterior, Anterior and Lateral. The extrinsic muscles are the larger muscles which control the movement of the foot and the toes. On further exacerbation, this varus causes the insertion of the Achilles tendon to shift medially, giving further impetus to the condition. While starting off as a forefoot-driven phenomenon, the eventual dorsiflexion of the hindfoot then progresses into supination to become a varus.
High arches are common with the atrophy of the plantar intrinsic muscles especially the key ones in the forefoot such as the Abductor Hallucis, Flexor Hallucis Brevis and Adductor Hallucis. In the event of peripheral neuropathy, denervation of these muscles leads to a range of deformities such as hammer toes caused by the flexion of the interphalangeal joints and extension of the metatarsal-phalangeal joints and the appearance of prominent plantar metatarsal heads.
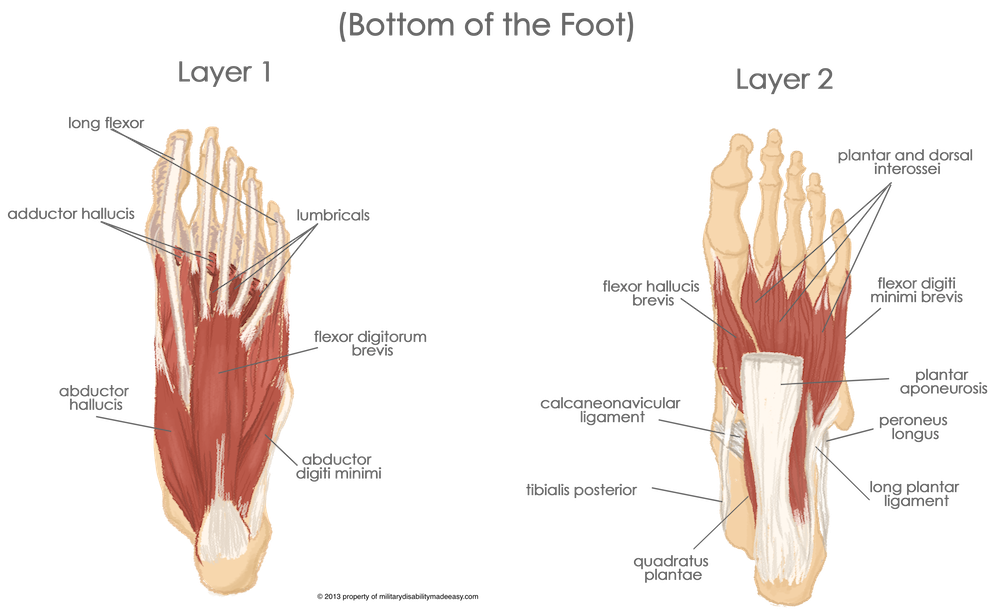
These studies prove vital in understanding the role played by these muscles in controlling foot posture, especially during weightbearing activities. Offer your Patients a Custom Calibrated Insole with a 98% Patient Satisfaction Rate know more Recent studies have shown that under external load, the activation of the three largest plantar intrinsic muscles - Abductor Hallucis, Flexor Digitorum and Quadratus Plantae - produces significant alterations in the metatarsal and calcaneus segment angles, helping to counter the deformation of the longitudinal arch (LA) by reducing the length and increasing the height of the LA.* The dorsal group of muscles is innervated by the deep fibular nerve while the tibial nerve, which innervates the plantar group, bifurcates into two branches - the medial plantar nerve and the lateral plantar nerve.
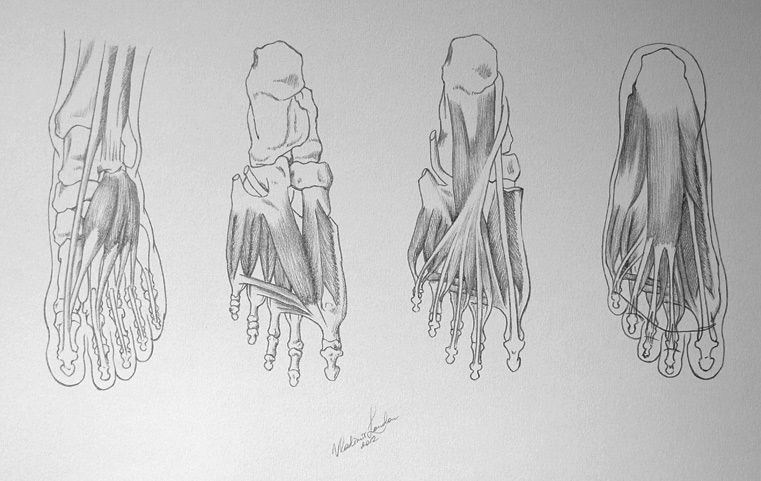
Two groups of these muscles exist - the plantar group located on the sole of the foot, which stabilises the arch and controls movement of individual digits, and the dorsal group located on the dorsum of the foot which assists some of the extrinsic muscles in their actions. The intrinsic muscles of the foot originate on the heel bone and work to stabilise the arches of the foot while regulating the rate of pronation and giving motion control to the foot.


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
